
Lastly, a large number of SSH clients on the market means that the security of the protocol also depends on the security of third-party apps.

Some malware programs attack IoT devices with ports exposed, using them as a backdoor entrance to the local network. This information includes accounts and resources, such as databases, routers, payment systems, etc.Įxposed SSH ports are another potential security weakness. While SSH keys offer better protection, their misuse can provide malicious individuals access to privileged information. However, poor SSH key management still presents a significant risk to organizations whose critical information depends on keeping the keys secret. SSH keys are recommended as a more secure authentication method than passwords. When they gain access to a server, they use privilege escalation to gain access to the root account. Attackers attempt to connect to a large number of SSH servers using common usernames and passwords. However, human factors play a significant role in maintaining the security of SSH connections.īrute force attacks on SSH servers are a common scenario. When used with standard security precautions, the SSH protocol is considered to be highly secure.
SSH SHELL NJIT WINDOWS
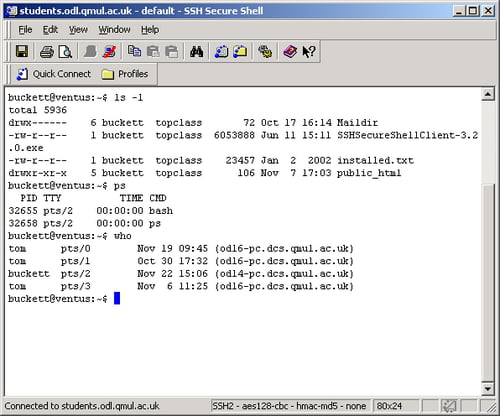
Some other popular SSH clients for Windows include: To connect to a remote host using the terminal, the user issues the ssh command followed by the username and the server address or hostname: ssh example: On these systems, the SSH client is available in the terminal. Most Unix-based and Unix-like operating systems come with the daemon and the client preinstalled.
SSH SHELL NJIT HOW TO
How to Use SSH?Ĭonnecting to an SSH server is performed using an SSH client.

SSH keys are often employed in automating server access with passwordless login, configuration management, and backup.
SSH SHELL NJIT SOFTWARE
SSH is widely used in data centers to provide secure management, remote access to resources, software patches, and updates. The layer of the SSH protocol overlooking the entire SSH session. Secure File Transport Protocol - a protocol using SSH to secure network file transfers, not to be confused with FTPS, which leverages TLS/SSL Secure Copy - a CLI utility that utilizes SSH for secure file transfer. Part of the public-private key pair for user authentication copied to the SSH server during the authentication process.Ī computer running an SSH server to which SSH clients connect.Ī user accessing SSH over a remote computer.Īn SSH server program for communicating with SSH clients.
Part of the public-private key pair for user authentication kept as a secret on the local machine. The layer of the SSH protocol that manages communication channels.Ī computer running an SSH client at the location.Ī user accessing SSH over the local computer. The layer responsible for conducting the SSH authentication.Ī client program for establishing a connection with the server. The following table contains some terms you may encounter when working with SSH: TermĪ user's home directory on a Unix or Unix-like system. The support for SSH-1 has been discontinued. As of version 7.6, OpenSSH supports only SSH-2. The OpenBSD developers later forked OSSH to create OpenSSH, the most popular SSH implementation in the world today. The open-source community developed OSSH, an SSH protocol version based on version 1.2.12 of SSH-1. In 2006, SSH-2 became a new standard, featuring security improvements such as Diffie-Helman key exchange. It started as freeware but soon became proprietary software.Īfter Ylönen's SSH-1 became a popular tool worldwide, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) assembled a group whose purpose was to develop a successor to the protocol. The first version of the protocol, now called SSH-1, was designed to replace unsecured protocols such as rsh, rlogin, and Telnet. The protocol was designed to prevent password-sniffing attacks at the Helsinki University of Technology. Note: For more information about the mechanism behind the SSH protocol, read How Does SSH Work? A Brief SSH History


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
